The purpose of a red team is to evaluate a company’s IT security posture without exposing it to risk from threat actors. These help organizations safely identify security flaws by conducting authorized, controlled “attacks” on an IT environment. They can then help make recommendations for fixing these vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them.
Red teams come in various forms. Below are some ways to distinguish between different types of red teams:
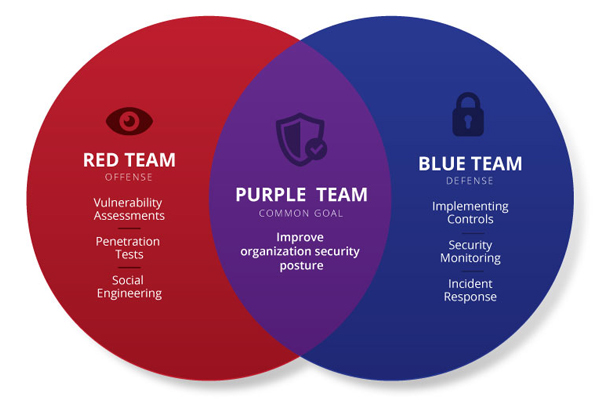
Red and blue team members often work together in what is known as a “purple team exercise”(Deloitte). In this exercise, both teams share their knowledge and expertise and receive real-time feedback about the effectiveness of attack and defense techniques.
During a purple team exercise, the red team works to execute its planned attack strategies while the blue team actively monitors and defends the target system. After the exercise, both teams come together to analyze the results, identify gaps in the organization’s security, and collaboratively develop strategies to bolster defenses.
Red team exercises (or “red teaming”) are simulations or assessments designed to evaluate an organization’s IT security structure by placing it under stress or attack. The major goal is identifying and resolving potential vulnerabilities malicious actors can exploit.
Red teaming usually includes several stages from start to finish:
Analyzing the result of the attacks and making recommendations to improve IT security
Below are some examples of different red team exercises:
The major advantages include:
One example of how red teaming helps organizations comes from Dionach, an IT security provider. A large multinational company in the financial technology industry recently contracted Dionach to conduct a red team assessment of its IT environment.
The exercise uncovered serious issues with the company’s network and physical security. In addition, Dionach identified various malicious actions that were not detected by the company’s alerting and monitoring software. Dionach worked with the client to fine-tune its monitoring devices so that similar attacks would now be detected (Dionach).
Each IT professional has a different red team career path. Some red team members may opt for computer science, information technology, or cybersecurity education. Others can accumulate expertise by learning on the job through hands-on experience. In contrast, many others may obtain red team certifications that verify their ability to detect and resolve security vulnerabilities.
EC-Council’s Ethical Hacking Essentials (E|HE) course is ideal for beginners to get started on their red team career path. Students learn the basics of ethical hacking across 12 modules, 11 hands-on lab activities, and more than 15 hours of premium self-paced video content with CTF challenges.
EC-Council’s Certified Ethical Hacker (C|EH) course is the world’s no1. ethical hacking and red teaming certification program for over 20 years. The program uses a unique Learn-Certify-Engage-Compete framework:
EC-Council’s Certified Penetration Testing Professional (C|PENT) program is the best penetration testing course for cybersecurity enthusiasts. The C|PENT certification teaches students about the industry’s best practices for penetration testing tools, techniques, and methods. C|PENT includes 14 theoretical and practical modules for detecting security vulnerabilities. Students learn about identifying weaknesses in various IT environments, from networks and web applications to the cloud and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.

Edutech Life is an ideology, a lifestyle, which makes sure that every career is fueled with the right tools. Be it getting proper guidance on the various Career tracks or how to follow the proper career steps or even upgrading on to a higher position.
Address : 205-206, 2nd Floor, Neelkanth Chambers-II, Plot No.14, LSC, Saini Enclave, Delhi-110092
Phone : +91-9599019927
Email : info@edutechlife.com
© 2022 Edutech Life. All rights reserved.
